Do GPU Fans Push or Pull – Understanding Your GPU Cooling System!
In the world of high-performance computing, especially for gaming, video editing, and intensive graphical tasks, keeping your GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) cool is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity.
One key component of this cooling system is the GPU fan. But how exactly does it work? Do GPU fans push or pull air, and why does it matter? This article will explore the mechanics of GPU fans, their role in cooling, and how to optimize your GPU cooling system.
The Basics of GPU Cooling:

Understanding GPU Fans
GPU fans are designed to manage the temperature of your graphics card by dissipating the heat generated during operation. The cooling system typically consists of the fan itself, heatsinks, and thermal paste. The fan’s primary function is to move air across the heatsinks, which absorb and dissipate the heat away from the GPU core.
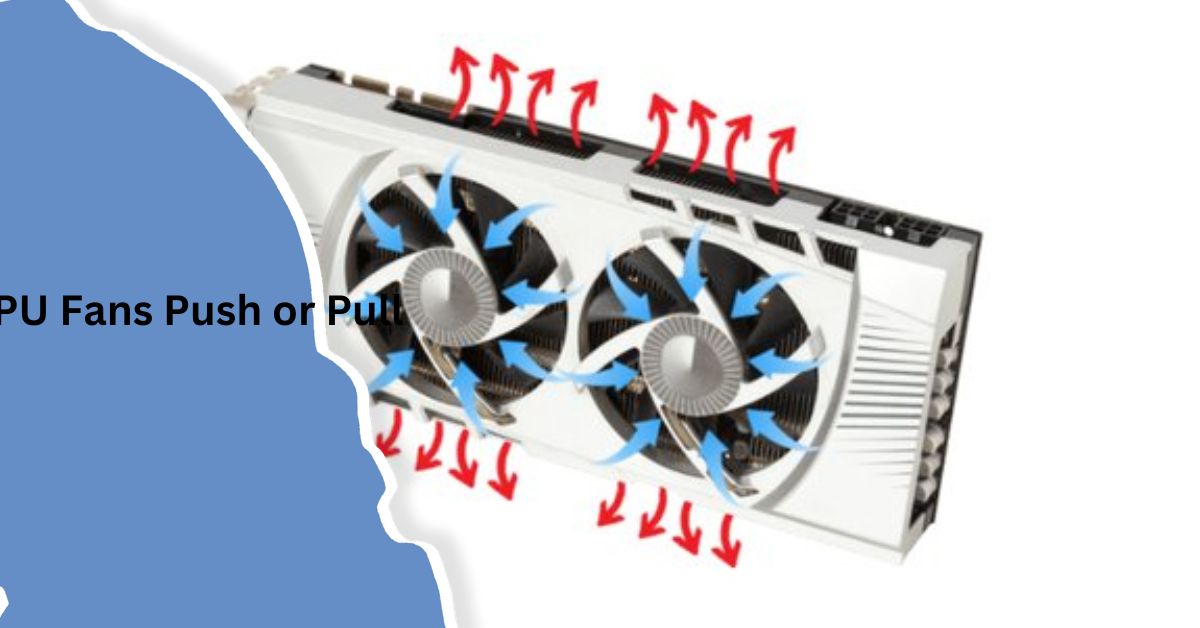
Push vs. Pull Configuration
The terms “push” and “pull” refer to the direction in which the fan moves air:
- Push Configuration: In this setup, the fan blows air towards the heatsink or GPU, pushing warm air away from the GPU and allowing cooler air to reach the heatsink.
- Pull Configuration: Here, the fan pulls air away from the heatsink, drawing warm air off the GPU and allowing cooler air to replace it.
Importance of Fan Direction
The direction of airflow can significantly impact the efficiency of the cooling system. Proper airflow ensures that the GPU remains within safe temperature limits, which is crucial for both performance and hardware longevity.
Also Read: Ps5 Performance Can Be Equal To Which Gpu – Compare Ps5 To Gpus!
How GPU Fans Work?
Airflow Mechanics
GPU fans are usually mounted on the card’s heatsink and operate in one of the following ways:
- Blower Style Fans: These fans push air through the heatsink and expel it out the back of the GPU. This design is effective for cooling but can be noisy.
- Axial Fans: These are the most common type of GPU fans. They can be configured to either push or pull air through the heatsink, depending on the design of the GPU cooler.
Push Configuration in GPUs
In a push configuration, the fan is oriented to direct airflow towards the heatsink. This setup is beneficial because:
- Increased Airflow to Heatsink: It pushes cooler air directly onto the heatsink, which can improve heat dissipation.
- Enhanced Cooling Efficiency: More efficient cooling can be achieved if the surrounding airflow is well managed.
Pull Configuration in GPUs
In a pull configuration, the fan draws air away from the heatsink. This setup provides several advantages:
- Reduction of Air Pressure: Pulling air away can create a negative pressure environment, which may help in pulling warmer air out of the system more effectively.
- Cleaner Airflow Path: It can sometimes reduce turbulence and improve the airflow path through the heatsink.
Can I change the direction of my GPU fan?
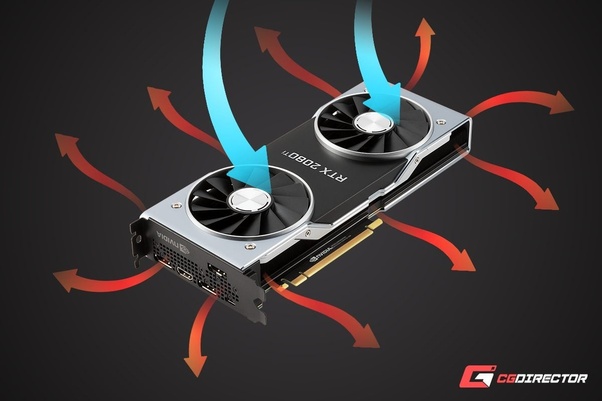

Changing the direction of your GPU fan can be tricky because most GPU fans are fixed in one position. The fan blades are designed to either push air through the heatsink or pull it away, and altering this setup usually requires physical modification, which is not only complex but could also void your warranty. If you need better airflow, consider improving case ventilation or using aftermarket cooling solutions designed for better performance without having to alter the fan direction.
Practical Tips for Optimal GPU Cooling:
Regular Maintenance
Regardless of the fan configuration, it’s essential to maintain your GPU cooling system regularly. Dust buildup can obstruct airflow and reduce cooling efficiency. Clean your fans and heatsinks periodically to ensure optimal performance.
Monitor Temperatures
Use monitoring software to keep an eye on your GPU temperatures. This will help you determine if your current fan configuration is effective or if adjustments are needed.
Experiment with Configurations
If you have the flexibility, experiment with different fan configurations to find the setup that works best for your system. Each setup may offer different benefits based on your specific hardware and cooling needs.
Do GPU fans always spin?
GPU fans don’t always spin. They usually only start spinning when the GPU gets hot, spinning faster as the temperature rises. When the GPU is cool or not under heavy load, the fans may spin slowly or stop altogether to keep noise levels down.
How to Determine the Best Fan Direction for Your GPU?
Assessing Your GPU’s Cooling Design
To determine the best fan direction for your GPU, you should consider the following:
- Type of GPU Cooler: Check if your GPU uses a blower-style fan or an axial fan. Each type may have different optimal configurations.
- Case Airflow: Ensure that your PC case has good airflow. In cases with limited airflow, a pull configuration might be more effective.
Evaluating Performance and Noise
Different fan configurations can affect both cooling performance and noise levels. Testing various configurations and monitoring temperatures can help you find the optimal setup for your specific needs.
Do graphics card fans push the air from the GPU or pull the air to the GPU?
Graphics card fans can either push air through the heatsink or pull air through it. In a push setup, the fan blows air through the heatsink to move warm air away from the GPU. In a pull setup, the fan draws air through the heatsink, pulling hot air away from the GPU. Some systems use both methods to improve cooling. The choice affects how well the GPU stays cool and performs.
How can I reduce GPU fan noise?

learn the Fans and Heatsinks:
Dust and debris can cause the fans to work harder and become noisier. Regularly cleaning the GPU fans and heatsinks helps maintain efficient airflow and reduces noise.
Improve Case Airflow:
Ensuring good airflow within your computer case helps keep temperatures down and can reduce the need for fans to spin at high speeds. Consider adding or rearranging case fans for better ventilation.
Adjust Fan Speeds:
Use software tools like MSI Afterburner or GPU-Z to adjust the fan speeds manually. Lowering the fan speeds can reduce noise, but make sure not to let temperatures get too high.
Upgrade to Quieter Fans:
If your GPU’s stock fans are too noisy, you can replace them with quieter aftermarket fans. These fans are designed to be more efficient and less noisy.
Use GPU Undervolting:
Reducing the voltage to your GPU can lower its power consumption and heat output, which in turn can reduce fan speeds and noise. Tools like MSI Afterburner can help with undervolting.
Optimize Fan Profiles:
Many GPUs come with software that allows you to create custom fan profiles. Set a more gradual fan curve so that the fans only ramp up to higher speeds when temperatures reach a certain threshold.
Apply Thermal Paste:
Reapplying high-quality thermal paste can improve heat transfer from the GPU to the heatsink, potentially reducing the need for high fan speeds.
Use Vibration Dampeners:
Installing vibration dampeners can help reduce noise caused by fan vibrations. These can be added between the fans and the GPU mounting points.
Also Read: Is BRAW GPU Accelerated – The Ultimate Guide!
Do bottom fans help GPU?
Yes, bottom fans can help the GPU by improving overall airflow in the case. They draw cool air from the bottom of the case and direct it towards the GPU and other components. This additional airflow can help lower the GPU’s temperature, which may enhance its performance and longevity. Proper case ventilation, including the use of bottom fans, contributes to more effective cooling and can prevent overheating issues.
FAQ’s:
1. Can GPU fans affect overall system noise?
Yes, fans with higher RPMs or less efficient configurations can generate more noise. Balancing fan speed and cooling performance with noise levels is important for a quieter system.
2. Which fan configuration is better for gaming PCs?
Push configurations are often preferred for gaming PCs as they provide efficient airflow through the heatsink, enhancing cooling performance under heavy loads.
3. Can I use both push and pull fans on the same GPU cooler?
Yes, hybrid configurations combining push and pull fans can offer superior cooling performance by maximizing airflow through the heatsink and improving heat dissipation.
4. What factors should I consider when choosing GPU fans?
Consider airflow (CFM), static pressure, fan size, RPM, and overall case airflow when selecting GPU fans to ensure effective cooling and system performance.
5. How does static pressure affect GPU cooling?
High static pressure fans are better at pushing air through dense heatsinks or restrictive environments, which can enhance cooling efficiency in tight spaces.
6. Are larger GPU fans always better?
Larger fans can move more air at lower RPMs, resulting in quieter operation, but they require sufficient space within the GPU cooler and may not always be suitable for all systems.
7. Can I switch between push and pull configurations easily?
Yes, you can switch between configurations by repositioning the fans on your GPU cooler. However, ensure that the new setup is compatible with your system and cooling requirements.
8. How do I maintain optimal GPU cooling performance?
Regularly clean your GPU fans and heatsinks, ensure proper case airflow, and monitor temperatures to maintain optimal cooling performance.
Conclusion:
Understanding whether GPU fans push or pull air is crucial for optimizing your cooling system. The direction of airflow can affect cooling efficiency, noise levels, and overall performance. By choosing the right configuration and maintaining your GPU cooling system, you can ensure that your graphics card remains cool and performs at its best.
Read More:










Post Comment