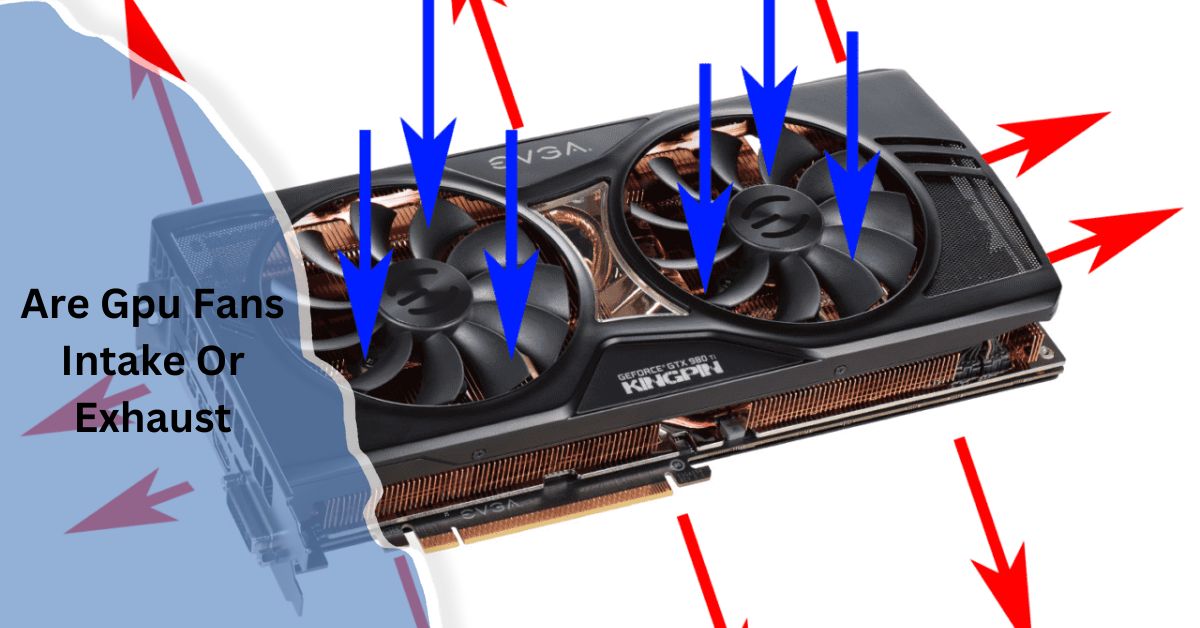
When building or upgrading a gaming PC, understanding how GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) fans work is essential for optimizing performance and maintaining a cool system. One common question people ask is whether GPU fans act as intake or exhaust fans.
GPU fans typically work as exhaust, meaning they push hot air out of the GPU to keep it cool. This helps prevent heat buildup inside the case. In some setups, fans can be configured as intake, but exhaust is more common for efficient cooling.
This guide will provide an in-depth look into GPU fan airflow, the role of intake and exhaust fans, and the best fan configuration for your system.
What is a GPU?

A Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a specialized processor designed to accelerate rendering graphics for displays. GPUs are essential for gaming, video editing, and high-performance computing tasks. Modern GPUs are equipped with fans to prevent overheating and ensure smooth performance by dissipating the heat generated during intensive workloads.
Types of GPU Fans:
There are two main types of GPU cooling solutions: blower-style and open-air fans. Both have their advantages and use different approaches to managing airflow within your PC case.
- Blower-Style Fans: These fans pull cool air into the GPU and expel hot air out through vents in the back of the card. They are ideal for cases with limited airflow.
- Open-Air Fans: These fans distribute hot air throughout the case rather than expelling it outside, requiring good case ventilation to avoid overheating.
How Do GPU Fans Work?
GPU fans are responsible for cooling the card by moving air over the heatsink, which absorbs heat from the GPU. However, there’s often confusion about whether these fans act as intake or exhaust.
Are GPU Fans Intake or Exhaust?
In most cases, GPU fans act as exhaust fans, pulling cooler air from the surrounding environment and pushing it over the GPU components to expel hot air. This configuration helps to move heat away from the GPU and other internal parts of the system, keeping temperatures manageable during intensive use.
The Direction of the GPU Fan Blades
The direction of the fan blades helps determine airflow. The blades are usually angled so that air is drawn from the underside of the card and pushed toward the heat-producing components. When the fan spins, it pulls air in from the bottom and pushes it toward the heatsink, facilitating heat dissipation.
The GPU Fan Housing and Vents
Most modern GPUs are equipped with heatsink fins and venting that guide airflow effectively. The fan housing plays a critical role in maintaining airflow efficiency. The placement of these components ensures that air is exhausted out of the rear or sides of the card, depending on the design.
Why is Exhausting Hot Air Important?
Hot air buildup inside a case can lead to decreased system performance, thermal throttling, or, in extreme cases, permanent damage to hardware components. Having an exhaust mechanism ensures that hot air generated by the GPU does not get recirculated, which could cause the overall system temperature to rise.
In Which Direction Does Air Flow Through a GPU?
For most open-air fan designs, air is pulled in from the case and expelled through the sides of the GPU. On blower-style fans, air is drawn in from the case and vented directly out of the back, providing a more controlled airflow that prevents heat from accumulating inside the case.
Choosing Fan Configuration: Key Factors
When deciding on a cooling strategy, whether to use GPU fans as intake or exhaust is influenced by several factors:
Case Design
Your PC case layout and airflow system will determine the best fan setup. Cases with poor ventilation might benefit more from GPUs configured to exhaust air out.
System Workload
Heavier workloads generate more heat, making a proper cooling configuration crucial for avoiding thermal throttling.
Additional Cooling
Fans in the rest of the case play a vital role. Proper intake and exhaust fan setups elsewhere help manage overall airflow more efficiently.
GPU Fans as Intake: Pros and Cons
While less common, some users opt to configure their GPU fans as intake, allowing cool air from outside the case to blow directly onto the GPU. Here are some pros and cons of this configuration:
Pros
- Improved Thermals: Intake configurations may lower the GPU’s temperatures by drawing in cooler air from outside the case.
- Prevents Recycling of Hot Air: By directing cool air into the GPU, this setup can prevent the recirculation of already heated air from within the case.
Cons
- Requires Good Case Cooling: For intake fans to work effectively, the case must have sufficient exhaust ventilation to remove the hot air that builds up.
- More Dust Buildup: Intake fans can increase dust accumulation in the GPU and case, which may necessitate more frequent cleaning.
GPU Fans as Exhaust: Pros and Cons
Using GPU fans as exhaust is the standard practice for most configurations, and there are several reasons why:
Pros
- Efficient Heat Removal: Exhaust fans are designed to quickly and effectively remove hot air from the GPU, maintaining lower internal temperatures.
- Prevents Overheating: As the hot air is expelled outside the case, it reduces the chances of system-wide heat buildup.
Cons
- Less Direct Cooling: While efficient for overall heat removal, this configuration does not directly blow cooler air onto the GPU itself.
- Potential Negative Pressure: If the number of exhaust fans outweighs intake fans, negative pressure can occur, pulling in unfiltered air and dust into the case.
How Do I Know If My GPU Fan is Intake or Exhaust?
To determine whether your GPU fans are set as intake or exhaust, you can check the orientation of the fan blades and the airflow pattern. Most GPUs are designed with exhaust fans by default, which means they pull air from inside the case and expel it out through the sides or back. You can also consult your GPU’s manual or use airflow testing methods, such as holding a small piece of paper near the fan to observe air direction.
FAQ’s:
1. What does it mean if my GPU fans are running as intake?
Intake fans pull cooler air from outside the case to cool the GPU, but require good case airflow to manage heat.
2. Should I set my GPU fans as intake or exhaust?
Most GPUs are best as exhaust, but intake can improve cooling with proper ventilation.
3. How can I tell if my GPU fans are configured for intake or exhaust?
Check fan blade direction or hold a paper near the fan to observe airflow; most are set for exhaust.
4. What are the advantages of GPU exhaust fans?
Exhaust fans remove hot air, helping prevent heat buildup and maintain stable performance.
5. Can changing my GPU fan setup improve performance?
Optimizing fan setup with good case airflow can reduce temperatures and boost performance.
6. Do blower-style GPUs have intake or exhaust fans?
Blower-style GPUs have exhaust fans, expelling hot air out the rear for controlled airflow.
7. Are intake GPU fans more prone to dust buildup?
Yes, intake fans can pull in more dust, requiring more frequent cleaning.
8. Is it better to have more intake or exhaust fans in a PC build?
A balanced intake and exhaust fan setup is ideal for optimal airflow and heat management.
9. How does the fan direction affect GPU cooling?
Fan direction determines whether air is drawn in or expelled, affecting heat dissipation.
10. Can case fans impact GPU fan efficiency?
Yes, balanced case fans improve GPU cooling by optimizing overall system airflow.
Final Thoughts:
The proper configuration of GPU fans can significantly impact your system’s overall performance and longevity. While most GPUs operate with exhaust fans, understanding your specific cooling needs and the airflow within your case can help you choose the optimal setup. Whether using GPU fans as intake or exhaust, ensuring efficient heat dissipation is crucial to maintaining a cool, stable, and high-performing PC.