What is a Good GPU Clock Speed – Check Your GPU Speed!
When it comes to building or upgrading a computer for gaming, video editing, or other intensive applications, one of the most critical components to consider is the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). Among the various specifications of a GPU, clock speed is one of the most talked-about metrics. But what exactly does it mean, and how can you determine what a good GPU clock speed is for your needs?
A good GPU clock speed generally depends on its type and use. For casual gaming, a speed around 1,200 to 1,500 MHz is suitable, while mid-range GPUs should be between 1,500 and 1,800 MHz. High-end GPUs often exceed 1,800 MHz for optimal performance in demanding tasks.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of GPU clock speed, its impact on performance, and provide insights to help you make informed decisions.
What is GPU Clock Speed?
Definition of Clock Speed
Clock speed, measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz), refers to the frequency at which a GPU’s cores can perform operations. Essentially, it indicates how many cycles per second the GPU can execute, impacting its overall processing power. A higher clock speed typically means a GPU can perform more calculations in a given time frame, leading to better performance in tasks such as gaming, rendering, and other graphic-intensive applications.
Base Clock vs. Boost Clock
Most modern GPUs have two distinct clock speed metrics: the base clock and the boost clock.
- Base Clock: This is the minimum speed at which the GPU operates under standard conditions. It represents the speed the GPU maintains when performing light tasks or when it is not under heavy load.
- Boost Clock: This is the maximum speed the GPU can achieve under optimal conditions, typically when temperatures and power consumption allow for it. The boost clock is crucial for demanding tasks, as it enables the GPU to handle intensive workloads effectively.
Understanding the difference between these two speeds can help you gauge how a GPU will perform in various scenarios.
Importance of GPU Clock Speed:
Impact on Gaming Performance
In gaming, clock speed plays a vital role in determining frame rates and overall performance. Higher clock speeds allow the GPU to render frames more quickly, providing smoother gameplay and a more responsive experience. However, it’s important to note that clock speed is not the sole factor influencing gaming performance. Other elements, such as the number of cores, architecture, and memory bandwidth, also significantly affect how well a GPU can perform.
Relation to Other Specifications
While clock speed is an essential factor, it works in conjunction with other specifications. For instance, a GPU with a high clock speed but fewer cores may not outperform a GPU with a slightly lower clock speed but more cores. The architecture of the GPU also matters; newer architectures tend to be more efficient, allowing them to deliver better performance at lower clock speeds compared to older models.
What is Considered a Good GPU Clock Speed?
General Guidelines
Determining what constitutes a “good” GPU clock speed can be subjective, as it largely depends on the intended use of the GPU. Here are some general guidelines:
- Entry-Level GPUs: For budget-friendly options, clock speeds around 1,200 to 1,500 MHz (1.2 to 1.5 GHz) are common. These GPUs are suitable for casual gaming and everyday tasks.
- Mid-Range GPUs: A good clock speed for mid-range GPUs typically falls between 1,500 and 1,800 MHz (1.5 to 1.8 GHz). This range offers a balance between performance and affordability, making these GPUs suitable for gaming at 1080p with decent settings.
- High-End GPUs: High-end graphics cards often boast clock speeds exceeding 1,800 MHz (1.8 GHz) and can reach up to 2,500 MHz (2.5 GHz) or more in boost clock speeds. These GPUs are designed for 4K gaming, demanding applications, and professional creative work.
Examples of Good GPU Clock Speeds
To provide context, here are a few examples of popular GPUs and their clock speeds:
- NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1650: Base clock of around 1,485 MHz and boost clock up to 1,665 MHz.
- AMD Radeon RX 6600: Base clock of 1,062 MHz and boost clock reaching up to 2,589 MHz.
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080: Base clock of approximately 1,440 MHz with a boost clock of around 1,710 MHz.
These examples illustrate how clock speeds can vary significantly between different GPU models and tiers.
Factors Influencing GPU Clock Speed:
Cooling Solutions
One of the critical factors that can impact a GPU’s clock speed is its cooling solution. Effective cooling allows the GPU to maintain higher clock speeds for extended periods without overheating. Many modern GPUs come equipped with advanced cooling systems, including multiple fans, heat sinks, and even liquid cooling solutions, all designed to keep temperatures in check.
Power Supply
The power supply unit (PSU) also plays a crucial role in a GPU’s performance. Insufficient power can limit a GPU’s ability to reach its maximum clock speed. Ensuring your PSU meets or exceeds the recommended wattage for your GPU is essential for optimal performance.
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of manually increasing a GPU’s clock speed beyond its factory settings to achieve higher performance. While overclocking can yield impressive gains, it also comes with risks, such as increased heat output and potential system instability. It’s vital to monitor temperatures and ensure adequate cooling when overclocking.
Monitoring and Benchmarking Clock Speed:
Using Software Tools
To understand how your GPU performs under different loads, you can use various software tools to monitor clock speeds and other metrics. Popular tools include:
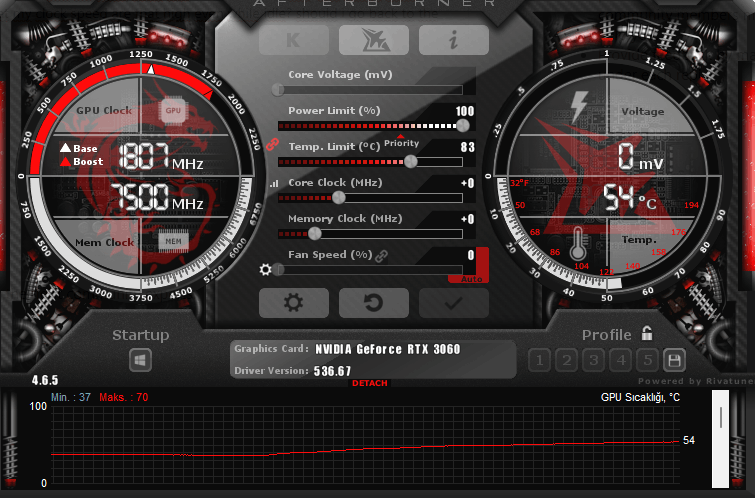
- MSI Afterburner: This widely used software allows users to monitor GPU performance, including clock speeds, temperatures, and usage percentages. It also offers overclocking capabilities.
- GPU-Z: A lightweight utility that provides detailed information about your GPU, including clock speeds, memory usage, and more.
- FurMark: A benchmarking tool that stresses your GPU and allows you to see how it performs under heavy load conditions.
Benchmarking Performance
Running benchmarks can help you assess how your GPU performs compared to others on the market. Websites like 3DMark and UserBenchmark provide scores and performance comparisons across a wide range of GPUs, helping you determine if your clock speeds align with expectations.
FAQ’s:
1. What is a GPU clock speed?
GPU clock speed refers to the frequency at which a GPU operates, measured in MHz or GHz. It indicates how many cycles the GPU can execute per second, affecting its overall performance.
2. What is the difference between base clock and boost clock?
The base clock is the minimum operating speed of a GPU, while the boost clock is the maximum speed it can achieve under optimal conditions. The boost clock is particularly important for handling demanding tasks.
3. What is considered a good clock speed for gaming?
A good clock speed for gaming varies by GPU tier. Entry-level GPUs usually range from 1,200 to 1,500 MHz, mid-range from 1,500 to 1,800 MHz, and high-end GPUs can exceed 1,800 MHz.
4. Does a higher clock speed always mean better performance?
Not necessarily. While a higher clock speed can lead to better performance, other factors such as core count, architecture, and cooling solutions also play a significant role.
5. How does cooling affect GPU clock speed?
Effective cooling allows a GPU to maintain higher clock speeds without overheating. Poor cooling can lead to thermal throttling, where the GPU reduces its speed to prevent damage.
6. Can I overclock my GPU for better performance?
Yes, overclocking can increase your GPU’s clock speed for enhanced performance. However, it comes with risks, such as increased heat and potential instability, so proper cooling and monitoring are essential.
7. How can I monitor my GPU clock speed?
You can use software tools like MSI Afterburner or GPU-Z to monitor your GPU’s clock speed, temperature, and performance metrics in real time.
8. What are some popular GPUs and their clock speeds?
Examples include the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1650 with a boost clock of around 1,665 MHz and the AMD Radeon RX 6600 with a boost clock up to 2,589 MHz.
9. How important is the power supply for GPU performance?
A sufficient power supply is critical for optimal GPU performance. Insufficient power can limit a GPU’s ability to reach its maximum clock speed.
10. What tools can I use for GPU benchmarking?
Tools like 3DMark and UserBenchmark are popular for assessing GPU performance and comparing it against other models on the market.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding GPU clock speed is essential for anyone looking to maximize their system’s performance, especially for gaming and creative tasks. While a higher clock speed generally translates to better performance, it is crucial to consider it alongside other specifications, such as the number of cores and GPU architecture.








Post Comment