Will My CPU Bottleneck My GPU – A Complete Guide!
Understanding the balance between your CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is crucial for optimizing your computer’s performance, especially for gaming and graphics-intensive tasks.
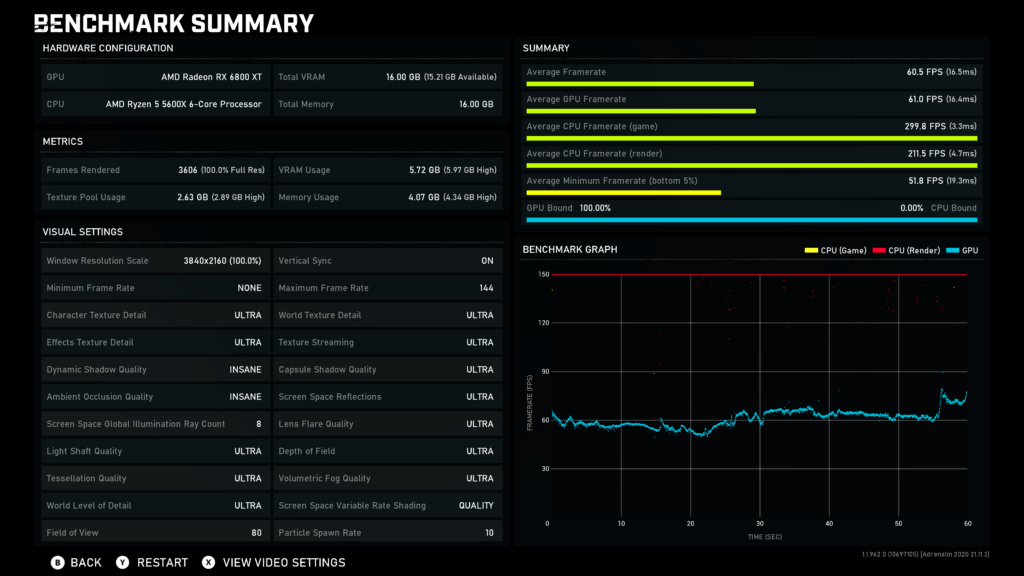
A CPU bottleneck happens when your processor is too slow compared to your GPU, limiting gaming or performance. If your CPU can’t keep up with your GPU, it can cause lower frame rates or stuttering. You can check by monitoring usage during tasks.
This comprehensive guide will explore what CPU bottlenecking is, how it affects your system, how to determine if it’s occurring, potential fixes, and tips for preventing future issues.
What is CPU Bottlenecking?
CPU bottlenecking occurs when a CPU cannot keep up with the demands of the GPU, limiting the overall performance of your system. In this scenario, the CPU becomes the weak link, preventing the GPU from performing at its full potential, which can lead to subpar gaming experiences and lower performance in applications.
How CPU Bottlenecking Affects Performance?
1. Lower Frame Rates
When the CPU cannot process data quickly enough, it can lead to a significant drop in frame rates during gaming. This results in a choppy visual experience, as the GPU is ready to render frames that the CPU hasn’t processed yet.
2. Stuttering and Lag
A bottleneck can cause noticeable stuttering and lag, particularly in fast-paced games. This happens when the CPU struggles to keep up with the GPU, leading to uneven frame delivery and a frustrating gaming experience.
3. System Instability
In severe cases, CPU bottlenecking can lead to system instability, including crashes and freezes. If the CPU is overwhelmed, it may fail to communicate effectively with other components, leading to overall performance degradation.
Also Read: Usps Broken Gpu – A Comprehensive Guide!
How to Determine if Your CPU is Bottlenecking Your GPU?
Monitoring CPU and GPU Usage
Download and Install Monitoring Software
To assess whether your CPU is bottlenecking your GPU, use monitoring software like MSI Afterburner, HWMonitor, or Task Manager. These tools provide real-time data on CPU and GPU usage.
Configure Monitoring Settings
Set up the monitoring software to display CPU and GPU usage percentages, temperatures, and clock speeds. This data will help you identify any discrepancies between CPU and GPU performance.
Run a Graphics-Intensive Game
Launch a graphics-intensive game or application to put your hardware under load. This will provide a clear picture of how each component performs under pressure.
Observe Usage Patterns
While gaming, pay close attention to CPU and GPU usage. If the GPU is operating at near 100% while the CPU remains significantly lower, it’s a strong indicator of bottlenecking.
Using Performance Comparison Tools
Online tools and calculators can provide additional insights. For example:
GPU Check’s CPU-GPU Bottleneck Calculator
There are several online calculators available that estimate potential bottlenecks. Input your CPU and GPU models to receive an analysis of their performance compatibility.
Symptoms of CPU Bottlenecking:
Identifying the symptoms of CPU bottlenecking can help you address the issue promptly.
1. Decreased Frame Rates and Stuttering
If you notice a significant decrease in frame rates or experience stuttering during gameplay, your CPU may not be keeping pace with your GPU.
2. High CPU Usage and Low GPU Usage
Monitor the usage statistics: a consistently high CPU usage coupled with low GPU usage during gaming sessions can indicate a bottleneck.
3. System Crashes and Instability
Frequent system crashes or instability can result from a CPU that’s struggling to keep up with the demands placed on it by the GPU.
How to Fix CPU Bottlenecking?
1. Upgrade Your CPU
- Compatibility: If your CPU is significantly weaker than your GPU, upgrading to a more powerful CPU is the most effective solution. Ensure that the new CPU is compatible with your motherboard’s socket type and chipset before purchasing.
- Performance Matching: Choose a CPU that complements your GPU’s power. Matching their performance levels ensures that neither component is overwhelmed. Research benchmarks and performance reviews to select the right CPU for your system.
2. Adjust In-Game Settings
- Lower CPU-Intensive Settings: In many games, certain settings place a heavy load on the CPU. Reducing settings like shadows, view distance, AI, and physics calculations can ease the burden on your processor, reducing the bottleneck effect.
- Increase Resolution: Increasing your game’s resolution can shift more work to the GPU, balancing the load between the CPU and GPU. However, ensure that your GPU can handle the increased resolution without sacrificing performance.
3. Close Background Applications
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Background applications running simultaneously with your game or resource-heavy programs can drain CPU resources. Use Task Manager or similar tools to identify and close unnecessary programs before starting your game or intensive applications.
- Use Task Manager: Task Manager can be used to monitor CPU usage and close apps that are consuming significant resources, freeing up more processing power for your gaming or productivity tasks.
4. Overclock Your CPU
- Check Overclocking Compatibility: If your CPU supports overclocking, this can be an effective way to boost performance without upgrading. Overclocking involves increasing your CPU’s clock speed beyond its stock frequency to improve processing power.
- Monitor Temperatures: Ensure your cooling system is adequate, as overclocking generates additional heat. Use temperature monitoring tools to prevent overheating and potential damage to your CPU.
5. Upgrade to a Multi-Core Processor
Upgrading to a CPU with more cores and threads can help reduce bottlenecking in modern games and applications that are optimized for multi-core processing. This spreads the workload more evenly across cores, improving efficiency and reducing the strain on any single core.
6. Adjust System Power Settings
Ensure your computer is set to “High Performance” mode in the power settings. This will ensure that your CPU runs at its maximum potential rather than being throttled to save energy, which can cause unnecessary bottlenecks.
7. Update Drivers and Software
Keeping your system’s software up to date, including your CPU and GPU drivers, can help reduce bottlenecking. Driver updates can improve compatibility and efficiency between your components, ensuring they work together optimally.
8. Install a More Efficient Cooling System
If your CPU is overheating, it may throttle its speed to prevent damage. This reduces performance and exacerbates bottlenecking. Consider upgrading to a more efficient cooling solution like a higher-end air cooler or liquid cooling system to keep temperatures in check.
9. Monitor System Performance Regularly
Use performance monitoring tools like MSI Afterburner, HWMonitor, or CPU-Z to regularly check CPU and GPU usage. This will help you spot potential bottlenecks early and address them before they become significant issues.
Can GPU Bottleneck CPU?

While it’s more common for a CPU to bottleneck a GPU, there are scenarios where a GPU can bottleneck a CPU. This can happen in cases where the GPU is extremely powerful compared to the CPU, leading to performance limitations in CPU-intensive tasks.
Preventing CPU Bottlenecking in Future Builds:
1. Choosing Compatible Components
- Performance Balance: When building or upgrading your PC, ensure that your components are well-matched. Research the performance levels of CPUs and GPUs to create a balanced system.
- Future-Proofing: Consider future needs when selecting components. Investing in a slightly more powerful CPU can help prevent bottlenecking as software and games become more demanding.
Also Read: How to Boot Without GPU – GPU-Free Booting Guide!
2. Considerations for New Purchases
- Compatibility: Always check compatibility when purchasing new components. Ensure that your motherboard, RAM, and power supply can support the new CPU or GPU.
- Performance Benchmarks: Utilize performance benchmarks and reviews to guide your purchases. Look for comprehensive tests that highlight how CPUs and GPUs perform in real-world scenarios.
FAQ’s:
1. What is CPU bottlenecking?
CPU bottlenecking occurs when the CPU cannot process data fast enough to keep up with the GPU, limiting overall performance and causing issues like lower frame rates and stuttering.
2. How can I tell if my CPU is bottlenecking my GPU?
Monitor your CPU and GPU usage during gaming. If the GPU usage is high while the CPU remains low, it’s likely that the CPU is bottlenecking the GPU.
3. What are the symptoms of CPU bottlenecking?
Common symptoms include decreased frame rates, stuttering, high CPU usage with low GPU usage, and system instability or crashes.
4. Can I fix CPU bottlenecking?
Yes, you can fix it by upgrading your CPU, adjusting in-game settings, closing background applications, or overclocking your CPU.
5. What happens if my CPU bottlenecks my GPU?
If your CPU bottlenecks your GPU, it can lead to poor gaming performance, including lower frame rates and increased lag, resulting in a frustrating experience.
6. Is overclocking safe to fix bottlenecking?
Overclocking can improve performance but should be done carefully. Monitor temperatures closely to prevent overheating and damage to your CPU.
7. What should I consider when upgrading my CPU?
When upgrading, ensure compatibility with your motherboard and choose a CPU that matches your GPU’s performance to maintain balance.
8. Can a powerful GPU still bottleneck a CPU?
Yes, a powerful GPU can bottleneck a CPU in certain scenarios, especially when the CPU cannot handle the demands of the software or games being run.
9. How can I prevent CPU bottlenecking in future builds?
Choose compatible components, ensure a balanced performance level, and consider future needs when selecting CPUs and GPUs for your system.
10. Do I need special software to monitor CPU and GPU performance?
Yes, monitoring software like MSI Afterburner or Task Manager can help track CPU and GPU performance and identify potential bottlenecks effectively.
Closing Remarks:
Understanding the dynamics between your CPU and GPU is essential for achieving optimal performance in gaming and other graphics-intensive tasks. By monitoring usage, recognizing symptoms of bottlenecking, and taking appropriate measures, you can enhance your system’s efficiency and enjoy a smoother experience.
Read More:














Post Comment