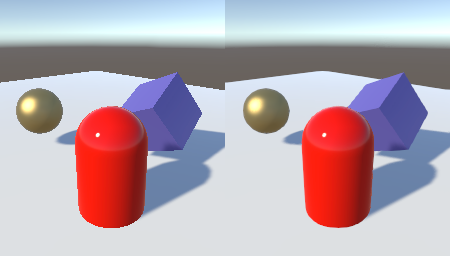
Is Anti Aliasing CPU or GPU – Optimize Your Game Setup!
In the world of gaming and digital graphics, achieving the best visual experience is crucial. Anti-aliasing plays a key role in enhancing the quality of graphics by smoothing out jagged edges, but a common question arises: Is anti-aliasing handled by the CPU or GPU?
Anti-aliasing is primarily handled by the GPU, which smooths out jagged edges in graphics. The CPU may play a minor role, but the heavy lifting is done by the GPU to enhance visual quality.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into understanding anti-aliasing, its importance, and how it interacts with both the CPU and GPU to provide you with clear insights and actionable advice.
What is Anti-Aliasing?

Anti-aliasing is a technique used in computer graphics to reduce visual distortions, known as aliasing, that can make edges of objects look jagged or pixelated. This method smooths out these rough edges, giving the graphics a more polished and realistic appearance.
Why Does Anti-Aliasing Matter?
Anti-aliasing is crucial for improving visual quality in both gaming and general graphics. Without it, images can appear harsh, with noticeable stair-like lines that detract from the immersive experience, especially in high-definition displays.
What Does Anti-Aliasing Do for Your Graphics?
The main function of anti-aliasing is to refine the visual presentation by blending the edges of pixels that would otherwise stand out sharply. This results in smoother transitions and a more cohesive look, which is particularly important in fast-paced games and high-resolution media.
How Does Anti-Aliasing Work to Improve Image Quality?
Anti-aliasing works by sampling the colors around the edges of objects and blending them to create a smoother appearance. Different types of anti-aliasing techniques achieve this in various ways, but the goal is always to enhance image quality by minimizing the appearance of jagged edges.
Also Read: Is My Motherboard Compatible with Any GPU – Here’s What You Need to Know!
Why is Anti-Aliasing Important in Gaming and Graphics?
For gamers and graphic designers, anti-aliasing is a crucial tool that enhances the realism and visual appeal of the content. It ensures that the images you see on screen are as true to life as possible, which is essential for both immersive gaming experiences and professional graphic work.
Which Devices Benefit from Anti-Aliasing?
Anti-aliasing is beneficial across a range of devices, from high-end gaming rigs to everyday smartphones. Here’s how different devices benefit:
- Computers and Laptops: High-resolution displays on computers and laptops benefit greatly from anti-aliasing, especially in gaming and graphic design applications.
- Gaming Consoles: Modern gaming consoles, with their powerful GPUs, utilize anti-aliasing to provide smooth and immersive gaming experiences on large screens.
- Smartphones and Tablets: As mobile gaming and high-definition media consumption grow, anti-aliasing helps maintain visual quality on smaller screens.
- Televisions and Monitors: For home theaters and gaming setups, anti-aliasing ensures that high-definition content looks its best, even on larger screens.
Types of Anti-Aliasing:
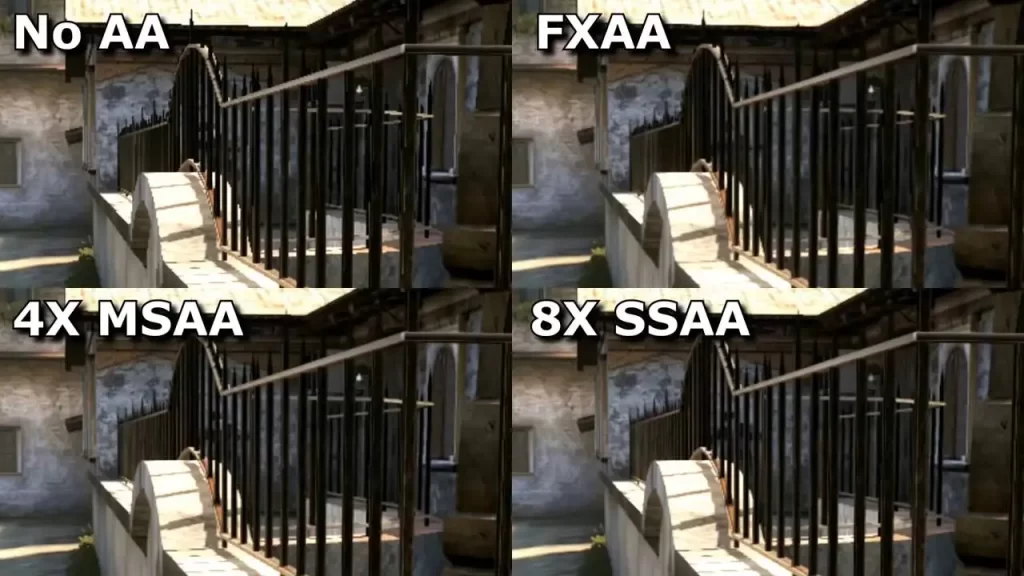

Different types of anti-aliasing techniques offer varying levels of quality and performance impacts. Here’s a look at some of the most common types:
1. MSAA (Multisample Anti-Aliasing)
MSAA is one of the most popular forms of anti-aliasing, offering a good balance between performance and visual quality. It samples multiple points along the edges of pixels to create a smoother appearance.
2. FXAA (Fast Approximate Anti-Aliasing)
FXAA is less demanding on hardware, making it ideal for mid-range systems. It works by smoothing out the entire image, which can sometimes result in a slightly blurred look.
3. TAA (Temporal Anti-Aliasing)
TAA uses information from previous frames to smooth out edges, reducing flickering and providing a stable image. It’s particularly effective in fast-paced games.
4. SMAA (Subpixel Morphological Anti-Aliasing)
SMAA is similar to FXAA but tends to preserve more detail, offering a good compromise between image clarity and performance.
5. SSAA (Super-Sampling Anti-Aliasing)
SSAA is the most effective but also the most resource-intensive type of anti-aliasing. It works by rendering the image at a higher resolution and then downscaling it, resulting in extremely smooth edges.
Is Anti-Aliasing Handled by the CPU or GPU?
Anti-aliasing is primarily handled by the GPU. The GPU is responsible for rendering graphics, and anti-aliasing is part of this process. The CPU may be involved in initial instructions or complex calculations, but the heavy lifting is done by the GPU.
How Anti-Aliasing Impacts CPU and GPU Performance?
- CPU Impact: The CPU’s role in anti-aliasing is limited. It might be involved in managing the overall game or application but doesn’t handle the rendering of anti-aliasing directly.
- GPU Impact: The GPU bears the brunt of the workload when anti-aliasing is enabled. Depending on the type of anti-aliasing used, this can significantly impact performance, as the GPU needs to process additional samples to smooth out edges.
What You Should Consider When Using Anti-Aliasing?
1. Performance Impact
Anti-aliasing can affect your system’s performance, particularly if you’re using an older GPU. It’s essential to find a balance between visual quality and smooth performance.
2. Graphics Settings
Different games and applications offer various anti-aliasing options. Experiment with these settings to find the one that works best for your system.
3. Compatibility
Some older games or hardware may not support certain types of anti-aliasing. Make sure your system and the games you play are compatible with the anti-aliasing technique you choose.
4. Balance
Achieving the right balance between visual quality and performance is key. Test different settings to see what works best for your needs.
Also Read: Update Graphics Driver Windows 11 Nvidia – A Complete Guide!
5. Personal Preference
Ultimately, the choice to use anti-aliasing comes down to personal preference. Some users prefer crisper images without any anti-aliasing, while others prioritize smooth edges.
6. Experimentation
Don’t be afraid to experiment with different types of anti-aliasing to see which provides the best results for your system and personal tastes.
FAQ’s:
1. What is the primary purpose of anti-aliasing in graphics?
Anti-aliasing is used to smooth out jagged edges in graphics, improving overall image quality and providing a more realistic visual experience.
2. Which is better: MSAA or FXAA?
MSAA offers better image quality with less blurring but requires more processing power than FXAA, which is less resource-intensive and faster but can make images look slightly blurred.
3. Does anti-aliasing affect FPS (frames per second)?
Yes, enabling anti-aliasing can lower FPS because it increases the GPU’s workload. The impact varies depending on the type of anti-aliasing used.
4. Can I use anti-aliasing on older GPUs?
You can use anti-aliasing on older GPUs, but the performance impact may be significant. Lower-intensity options like FXAA might be better suited for older hardware.
5. Is anti-aliasing necessary for 4K gaming?
In 4K gaming, aliasing is less noticeable due to the high pixel density, but some players still prefer to use anti-aliasing for an extra layer of smoothness.
6. How do I enable anti-aliasing?
You can enable anti-aliasing through in-game settings, your graphics card’s control panel, or specific software tools designed for this purpose.
7. Does anti-aliasing work on all types of monitors?
Yes, anti-aliasing works on all monitor types, though the level of effectiveness can vary depending on the monitor’s resolution and quality.
8. Can I adjust anti-aliasing settings on consoles?
Some gaming consoles allow you to adjust anti-aliasing settings, but options are usually more limited compared to PCs.
9. Should I use anti-aliasing for video editing?
Anti-aliasing can improve the visual quality of your video projects, particularly when working with high-resolution footage that includes fine details.
Conclusion:
Anti-aliasing is a powerful tool in the quest for better graphics, primarily handled by the GPU, and it plays a vital role in gaming and other visual media. While it can impact performance, the benefits of smoother, more realistic images often outweigh the drawbacks, especially when the right balance is found. By understanding how anti-aliasing works and how it interacts with your hardware, you can make informed decisions about which settings to use to enhance your visual experience.
Read More:












Post Comment