Discrete GPU is Idle – A Comprehensive Guide for Optimizing Your GPU Usage!
In today’s rapidly advancing world of technology, GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) have become an integral part of modern computing. GPUs are essential not only for gaming but also for tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, AI applications, and cryptocurrency mining. For many users, ensuring that their GPU is working efficiently is a priority.
“Discrete GPU is idle” means your dedicated graphics card isn’t being used, even when it could help with tasks like gaming or video editing. This could be due to system settings, driver issues, or power-saving modes. Fixing it ensures better performance for demanding tasks.
One common issue is when the “discrete GPU is idle,” which could indicate that the dedicated graphics card isn’t being utilized as intended. Understanding why this happens and how to resolve it can significantly improve performance.
What Does “Discrete GPU is Idle” Mean?
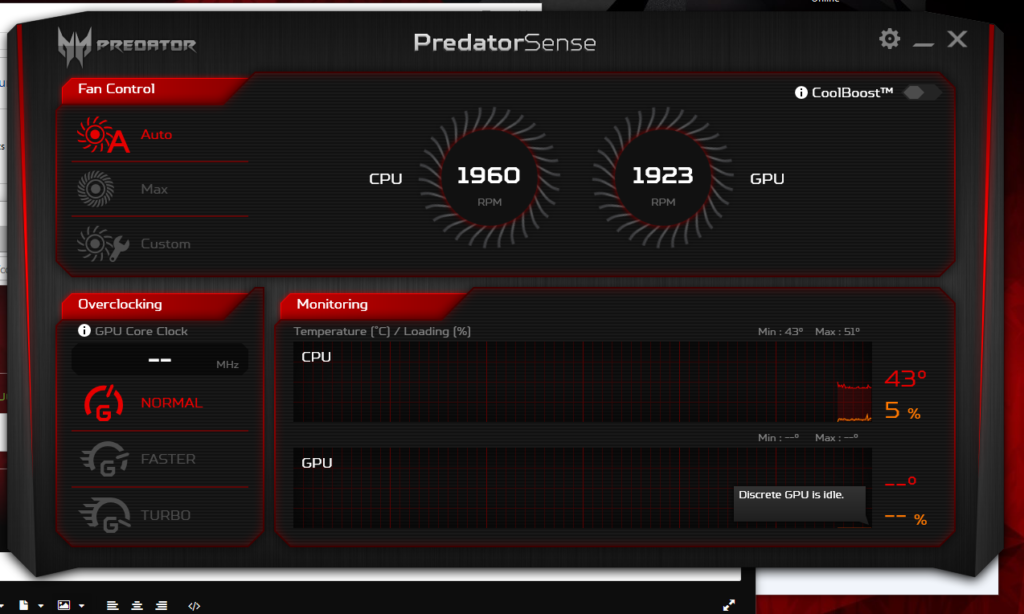
A discrete GPU is a standalone graphics card that operates independently of the CPU (Central Processing Unit). Unlike integrated GPUs, which are built into the CPU and share system memory, discrete GPUs have their own dedicated memory, offering superior performance for graphics-intensive tasks.
When a discrete GPU is “idle,” it means that the GPU is not actively performing any tasks. While this might be acceptable in certain circumstances (e.g., when the system is idle or performing tasks that do not require heavy graphics processing), it can be problematic if the GPU remains idle during activities that should engage it, such as gaming, video rendering, or using high-performance applications.
Reasons Why Your Discrete GPU May Be Idle:
- Software Settings or Misconfiguration: Sometimes, the reason for your discrete GPU idling is a misconfiguration in the system or application settings. Many systems default to using the integrated GPU for less demanding tasks and only switch to the discrete GPU when required. This switch may not always occur automatically if the settings aren’t correctly configured.
- Outdated or Improper Drivers: Using outdated drivers or having improperly installed drivers could prevent the system from recognizing or utilizing the discrete GPU. It’s crucial to ensure that the GPU’s drivers are up-to-date and properly installed to avoid this issue.
- Power Management Settings: Power management options, particularly in laptops, may prioritize energy efficiency over performance. If your system is set to a “power-saving” mode, it might choose to use the integrated GPU to conserve battery life, leaving the discrete GPU idle.
- Application Not Optimized for Discrete GPU Usage: Certain applications are not designed to leverage the power of a discrete GPU, particularly if they’re not graphics-intensive. In such cases, the discrete GPU remains idle because the system doesn’t require its enhanced performance capabilities.
- GPU Overheating or Hardware Issues: Overheating or other hardware malfunctions can cause the GPU to throttle or become idle to protect itself from damage. Monitoring your GPU’s temperature and ensuring that your cooling system is functioning properly is essential.
Also Read: Why Does Crt Filters Take So Much Gpu – A Deep Dive Into The Resource Demand!
How to Ensure Your Discrete GPU Is Being Used?
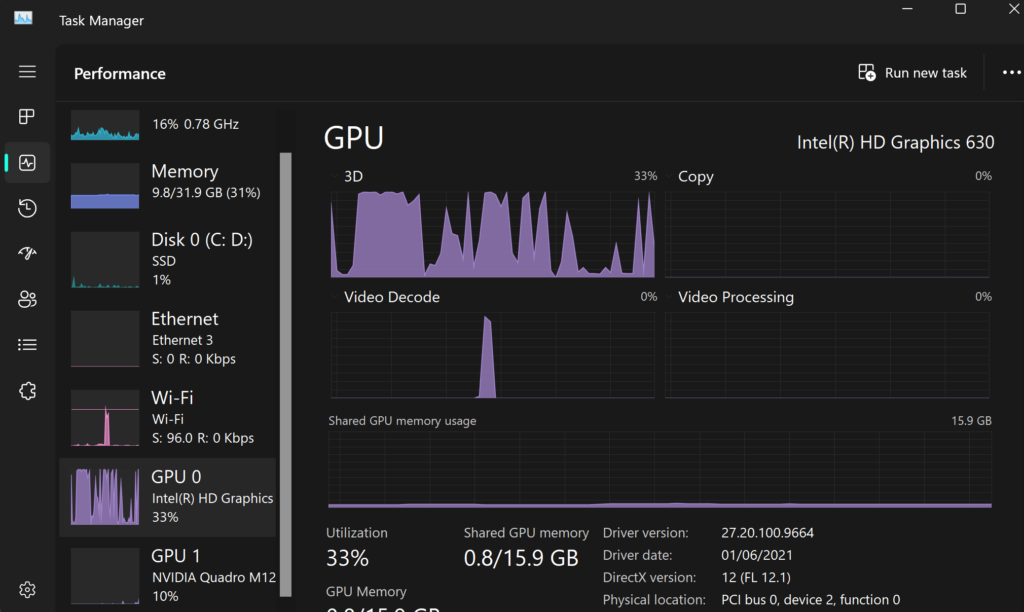
1. Optimizing System Settings
For many users, resolving the “discrete GPU is idle” issue can be as simple as adjusting system settings. Start by accessing the GPU control panel (such as NVIDIA Control Panel or AMD Radeon Software) and ensuring that the discrete GPU is set as the preferred option for high-performance tasks.
You may also want to manually assign specific applications to the discrete GPU. For instance, in the NVIDIA Control Panel, go to the “Manage 3D Settings” section, and under the “Program Settings” tab, select the desired program and set it to use the high-performance NVIDIA processor.
2. Updating and Installing Drivers
One of the first steps in troubleshooting GPU idling is checking your drivers. Visit the manufacturer’s website (such as NVIDIA or AMD) to download the latest drivers for your discrete GPU. Always uninstall outdated drivers before installing new ones to prevent conflicts or corrupted files.
Driver installation software can also help ensure that your system remains up-to-date with the latest versions, preventing compatibility issues that could cause the GPU to stay idle.
3. Adjusting Power Management Settings
For laptops or desktops with power-saving features, check your power plan settings. Go to “Power Options” in the Control Panel, and ensure that your plan prioritizes performance over energy efficiency. In the advanced settings, you can often find options that control GPU usage. Ensure that the discrete GPU is set to be used for high-performance tasks even when on battery power.
On systems with NVIDIA GPUs, the “Power management mode” setting can be adjusted within the control panel, allowing you to choose “Prefer maximum performance” instead of the default “Optimal power.”
4. Monitoring and Managing GPU Temperature
Excessive heat can cause your GPU to reduce its performance or become idle to prevent damage. Use monitoring tools such as MSI Afterburner or HWMonitor to keep an eye on your GPU’s temperature. If your GPU is running too hot, check your cooling solution, clean out any dust, and ensure that airflow within your system is optimized.
In more extreme cases, you may need to replace the thermal paste on your GPU to improve heat dissipation.
The Impact of an Idle Discrete GPU on Performance:
If your discrete GPU is idle, the most significant impact will be on performance. Tasks that would typically benefit from the enhanced processing power of the GPU will instead rely on the CPU or the integrated GPU. This could lead to:
- Lower Frame Rates in Games: An idle discrete GPU could result in stuttering, lower frame rates, and reduced visual quality in games that require high graphical processing.
- Longer Rendering Times: Video rendering and 3D modeling will take much longer to complete, as the CPU is far less efficient at these tasks compared to a discrete GPU.
- Reduced Efficiency in AI and Machine Learning: Computational tasks in AI and machine learning that could be accelerated by a discrete GPU may take longer, reducing overall productivity.
Applications and Games That Should Engage Your Discrete GPU:

Not all applications are designed to utilize a discrete GPU. Below are examples of software and games that typically demand the enhanced performance of a discrete GPU:
1. High-End Video Games
Titles such as Cyberpunk 2077, Call of Duty, and Red Dead Redemption 2 rely heavily on GPU performance for smooth gameplay, high frame rates, and detailed graphics.
2. Video Editing Software
Applications like Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and Final Cut Pro utilize GPU acceleration to handle rendering tasks more efficiently.
3. 3D Modeling and Rendering Tools
Programs such as Blender, AutoCAD, and Maya require the power of a discrete GPU to manage complex 3D models and render them quickly.
4. AI and Machine Learning Applications
Certain AI workloads, particularly those using frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch, are optimized to take advantage of GPU acceleration for faster computation times.
If your discrete GPU remains idle while running these types of programs, it could indicate an issue that needs to be resolved.
Also Read: Gpu Randomly Spikes To 100 When Idle 2080 Ti – Understanding And Resolving The Issue!
Preventing Discrete GPU Idling: Best Practices
To avoid the issue of your discrete GPU idling, consider the following best practices:
- Regularly Update Drivers: Keeping your GPU drivers up-to-date ensures that your system can make full use of the GPU’s capabilities.
- Monitor System Performance: Use performance monitoring tools to track GPU usage and temperature, so you can catch issues early.
- Prioritize High-Performance Settings: Adjust your system’s power management settings to favor performance over energy savings when needed.
- Assign Specific Programs to the GPU: Manually set demanding applications to use the discrete GPU to ensure optimal performance.
FAQ’s:
1. Why is my discrete GPU idle when gaming?
Your discrete GPU may be idle due to misconfiguration, outdated drivers, or power-saving settings. Ensure that the game is assigned to the discrete GPU and that your drivers are up-to-date.
2. How do I force my computer to use the discrete GPU?
You can force your computer to use the discrete GPU by adjusting the settings in your GPU’s control panel, such as NVIDIA Control Panel or AMD Radeon Software, and setting high-performance applications to use the discrete GPU.
3. Does an idle discrete GPU affect performance?
Yes, if your discrete GPU is idle during tasks that require heavy graphics processing, performance will be negatively affected, leading to lower frame rates, longer rendering times, and reduced efficiency in graphics-heavy applications.
4. Can overheating cause my discrete GPU to idle?
Yes, overheating can cause the GPU to throttle or become idle to prevent damage. Monitoring and managing the temperature with proper cooling solutions can prevent this issue.
5. What’s the difference between a discrete GPU and an integrated GPU?
A discrete GPU is a standalone graphics card with its own dedicated memory, offering superior performance for graphics-intensive tasks. An integrated GPU is built into the CPU and shares system memory, making it less powerful but more power-efficient.
6. Why is my laptop not using the discrete GPU?
Your laptop may default to using the integrated GPU for power-saving reasons. Check your power management settings and ensure that high-performance tasks are set to use the discrete GPU.
7. How do I check if my discrete GPU is being used?
You can check if your discrete GPU is being used by monitoring it through tools like Task Manager, MSI Afterburner, or HWMonitor, which show GPU usage statistics.
8. Can updating drivers solve the discrete GPU idle issue?
Yes, updating your drivers can often resolve issues related to the discrete GPU being idle by ensuring compatibility and correct system recognition of the GPU.
Closing Remarks:
Understanding the reasons why your discrete GPU might be idle is essential for ensuring optimal system performance. Whether it’s due to outdated drivers, improper settings, or power management configurations, addressing the root cause can unlock your GPU’s full potential. By following best practices and optimizing your system, you can ensure that your discrete GPU is always ready when needed, delivering the best performance possible.
Read More:









Post Comment