What Does OC Mean in GPU – Enhance Graphics Performance!
In the world of computing and gaming, GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are one of the most vital components for delivering stunning visuals and high-performance gameplay. Among the various terms used to describe GPU specifications, the acronym “OC” often surfaces. But what exactly does OC mean in a GPU, and why should it matter to you?
This article will explore the concept of OC (Overclocking) in GPUs, how it affects performance, its benefits, potential risks, and everything you need to know to make informed decisions about your GPU setup.
Understanding What OC Means in GPUs:
OC stands for Overclocking. Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed of the GPU beyond its factory settings to improve performance. It essentially pushes the GPU to operate at a faster rate than it was originally designed for, allowing it to process more frames per second, rendering games and other graphical tasks faster and more efficiently.
How Does Overclocking Work?
Overclocking involves increasing the GPU’s core clock and memory clock speeds. The core clock determines how fast the GPU processes data, while the memory clock dictates how quickly the GPU can access and use its onboard memory (VRAM).

When you overclock a GPU, you tweak these values to enhance performance, but it requires careful consideration of the following aspects:
- Power Consumption: Higher clock speeds demand more power.
- Temperature: Overclocking can increase heat production, requiring better cooling solutions.
- Stability: Overclocking can lead to system instability if pushed too far.
Why Do Manufacturers Sell OC GPUs?
Many manufacturers, including ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, and EVGA, offer factory-overclocked GPUs. These OC GPUs come pre-configured with higher clock speeds than the standard models. Factory overclocked GPUs are tested to ensure they can handle the increased performance without compromising stability, making them an excellent choice for users who want a boost in performance without the risks of manual overclocking.
Benefits of Overclocking a GPU:
1. Improved Gaming Performance
Overclocking your GPU can boost its clock speed, allowing it to process more data per second, which results in higher frame rates. This leads to smoother gameplay, especially in graphics-heavy titles, where every frame counts for a fluid experience. Gamers will notice reduced lag and screen tearing, making the gaming experience more immersive and enjoyable.
2. Faster Rendering Times
In graphic design, video editing, and 3D rendering, overclocking speeds up the GPU’s performance, allowing it to handle more complex calculations in less time. This results in faster rendering times for large files or detailed projects, significantly improving productivity. Creative professionals can work more efficiently, reducing waiting times and optimizing workflow.
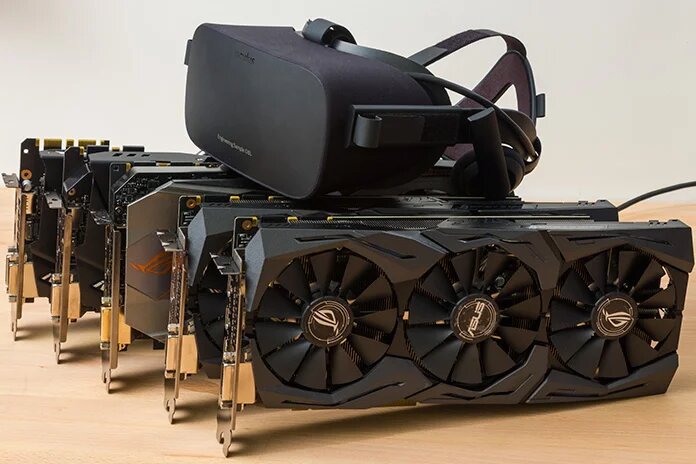
3. Enhanced VR Experiences
Virtual Reality (VR) applications are highly demanding on hardware, particularly when it comes to frame rates. Overclocking your GPU enables it to maintain the necessary frame rates, reducing motion sickness and lag in VR environments. This ensures that users can experience smoother, more immersive virtual reality, enhancing the overall experience with minimal interruptions.

4. Better Overall Efficiency
By overclocking, your GPU can achieve better performance without the need for expensive hardware upgrades. This improved efficiency allows users to maximize the potential of their current hardware, often bridging the gap between generations of technology. Overclocking offers a cost-effective solution for users seeking better performance in resource-intensive tasks without breaking the bank.
Risks of Overclocking:
- Increased Heat and Power Consumption: Overclocking leads to increased power consumption, which can cause higher temperatures. If not managed properly, this could lead to thermal throttling or hardware damage.
- Stability Issues: Pushing the GPU too far may result in system crashes, freezing, or artifacting in games. Stability tests are crucial to ensure smooth operation.
- Warranty Void: Manual overclocking could void the warranty of your GPU. Many manufacturers, however, offer factory-overclocked models that maintain their warranty.
- Shortened Lifespan: Consistent overclocking may reduce the lifespan of your GPU due to the stress on its components.
Should You Overclock Your GPU?
If you’re a gamer, content creator, or VR enthusiast seeking higher performance from your system, overclocking could be beneficial. However, the risks of overclocking need to be considered carefully.
- For Casual Users: If you’re satisfied with your GPU’s performance, overclocking may not be necessary.
- For Enthusiasts: Overclocking can unlock additional performance gains, but it requires patience, proper cooling, and a willingness to accept potential risks.
Factory Overclocked GPUs vs. Manual Overclocking:

1. Factory Overclocked GPUs
These GPUs are pre-tuned by manufacturers to run at higher clock speeds than standard models. They provide an easy way to enjoy enhanced performance without the complexity of manual overclocking. These GPUs are tested for stability, and typically, the manufacturer’s warranty remains intact.
2. Manual Overclocking
For those who enjoy tweaking hardware to achieve maximum performance, manual overclocking offers more control. Users can push the GPU further than factory OC settings, but they must be prepared to fine-tune settings to achieve the best balance of performance and stability.
How to Overclock a GPU?
- Choose Reliable Software: Tools like MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, and AMD WattMan allow you to adjust clock speeds, voltage, and fan speeds.
- Gradually Increase Clock Speeds: Start by increasing the core clock speed in small increments. After each adjustment, run benchmarks to test stability.
- Monitor Temperature: Use software like HWMonitor or GPU-Z to keep an eye on temperatures. Ensure that your GPU stays within safe operating temperatures.
- Adjust Memory Clock: After stabilizing the core clock, you can increase the memory clock for additional performance gains.
- Stress Test: Run stress tests using software like FurMark or 3DMark to ensure your overclock is stable under load.
Is overclocking a GPU safe?
Overclocking is generally safe when done carefully, but it can lead to higher temperatures and increased power consumption.

Adequate cooling is essential to avoid overheating and potential damage to the GPU.
FAQ’s:
1. What does OC mean in the context of GPUs?
OC stands for “Overclocked.” It refers to running a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) at a higher speed than its factory-set clock frequency to improve performance.
2. What is the purpose of overclocking a GPU?
The purpose of overclocking is to increase the GPU’s performance, allowing it to handle more demanding tasks such as gaming, video editing, or running intensive applications at higher frame rates or faster speeds.
3. How does overclocking a GPU work?
Overclocking works by increasing the clock speed of the GPU, which allows the processor to complete more calculations per second. This boosts performance but also generates more heat and may require better cooling.
4. Does overclocking void the GPU warranty?
Yes, overclocking can void the warranty of some GPUs. It’s important to check the manufacturer’s warranty terms before overclocking.
5. How can I overclock my GPU?
You can overclock a GPU using software like MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X, or other manufacturer-specific tools. These programs allow you to adjust the clock speeds and monitor temperatures.
6. Can every GPU be overclocked?
Most modern GPUs can be overclocked, but the potential performance gain varies depending on the model and manufacturer. Some GPUs are pre-overclocked by manufacturers and marketed as “OC” models.
7. Will overclocking a GPU improve gaming performance?
Overclocking can improve gaming performance by increasing frame rates and reducing lag in demanding games. However, the improvement may not be significant in all games or settings.
Closing Remarks:
Overclocking a GPU, whether factory-overclocked or manually tweaked, can significantly boost performance. However, it requires a balance of knowledge, the right tools, and an understanding of the risks involved. Always ensure that your system’s cooling and power supply are adequate to handle the increased load, and approach the process with caution.













Post Comment