GPU Manufacturers Tier List – An In-Depth Analysis!
In the competitive world of graphics processing units (GPUs), various manufacturers vie for dominance by offering products that cater to different needs—from gaming enthusiasts and creative professionals to AI researchers and everyday users. A GPU manufacturers tier list helps consumers navigate these choices by ranking companies based on performance, reliability, innovation, and value for money.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the key players in the GPU market, explore their strengths and weaknesses, and provide detailed insights into how they stack up against each other.
Understanding GPU Manufacturers:
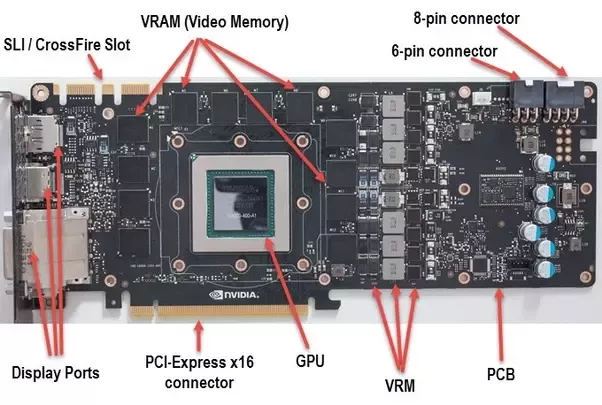
1. What is a GPU?
A Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a specialized processor designed to handle the complex calculations required for rendering images, video, and animations. GPUs are crucial for gaming, graphic design, video editing, and various other applications that demand high-performance computing.
2. Why a Tier List Matters
A GPU manufacturers tier list categorizes companies based on their product offerings, technological advancements, and overall market impact. This list serves as a valuable tool for consumers and professionals looking to make informed decisions when purchasing or upgrading their graphics hardware.
Top GPU Manufacturers:
1. NVIDIA
Overview: NVIDIA is widely regarded as the leader in the GPU market, known for its cutting-edge technology and high-performance products. The company’s GeForce series is a favorite among gamers, while the Quadro and Tesla series cater to professional and data center needs.
Strengths:
- Innovation: NVIDIA consistently pushes the envelope with features like real-time ray tracing and AI-enhanced graphics.
- Performance: High-end GPUs such as the GeForce RTX 4090 offer unmatched gaming and rendering performance.
- Software Support: NVIDIA’s drivers and software, including CUDA and DLSS, enhance performance and compatibility.
Weaknesses:
- Price: NVIDIA GPUs are often more expensive than competitors.
- Availability: High demand can lead to supply shortages.
2. AMD
Overview: AMD is a strong contender in the GPU market, offering competitive alternatives to NVIDIA’s products. The Radeon series is popular among gamers and professionals alike, with the RX 7000 series pushing the boundaries of performance.
Strengths:
- Value for Money: AMD GPUs often provide excellent performance at a lower price point than NVIDIA’s counterparts.
- Innovation: Features like FidelityFX and RDNA architecture contribute to high-quality visuals and performance.
- Compatibility: AMD’s GPUs work well with its CPUs, providing a balanced system performance.
Weaknesses:
- Driver Issues: AMD has faced criticism for driver stability and optimization.
- Feature Set: While improving, AMD’s feature set, such as ray tracing, is not as advanced as NVIDIA’s.
3. Intel
Overview: Intel, traditionally known for CPUs, has ventured into the GPU market with its Intel Arc series. Though a newcomer, Intel aims to challenge established players with innovative products.
Strengths:
- Integrated Solutions: Intel’s integrated graphics offer decent performance for everyday tasks and light gaming.
- Innovation: Intel’s Arc GPUs bring new technologies and features to the market.
Weaknesses:
- Early Stage: Intel’s GPU lineup is still evolving, with limited high-end options available.
- Market Penetration: Intel has yet to establish a strong presence in the high-performance GPU market.
4. Other Notable Manufacturers
- Qualcomm: Known for its Adreno GPUs in mobile devices, Qualcomm offers high-performance graphics for smartphones and tablets.
- ARM: ARM’s Mali GPUs are prevalent in mid-range and budget mobile devices, providing good performance for their price.
Also Read: https://www.techygpu.com/2024/11/17/why-is-my-gpu-not-connected-to-mystic-light/
Comparing GPU Manufacturers: Key Factors

Performance
When evaluating GPUs, performance is a critical factor. NVIDIA and AMD lead in this area, offering top-tier solutions for gaming, professional work, and data processing. Intel is still building its performance credentials but has shown promise.
Price
Price-to-performance ratio is vital for consumers looking to get the best value. AMD often leads in offering high performance at a more affordable price, while NVIDIA’s premium models come with a higher price tag.
Innovation
Innovation drives the GPU market, with NVIDIA and AMD competing on advanced technologies such as ray tracing and AI-enhanced features. Intel is making strides but is still catching up in this regard.
Software and Drivers
Stable and well-optimized drivers are essential for performance and compatibility. NVIDIA is known for its robust software support, including tools for gaming and professional applications. AMD is improving its driver support, but it has faced challenges in the past.
Availability and Support
The availability of GPUs can impact consumer choice, especially during high-demand periods. NVIDIA and AMD have established distribution networks, while Intel is still building its presence. Support and warranty services are also crucial considerations.
Are NVIDIA GPUs better for gaming than AMD GPUs?
- Performance and Features: NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX series, especially the higher-end models like the RTX 4090, delivers top-notch gaming performance with cutting-edge features such as real-time ray tracing and DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling). These technologies enhance visual fidelity and frame rates, making for a smoother and more immersive gaming experience.
- Ray Tracing Technology: NVIDIA pioneered real-time ray tracing, which simulates realistic lighting and shadows in games. This technology can significantly improve the graphical quality of games, although it requires substantial processing power.
- DLSS Technology: NVIDIA’s DLSS uses AI to upscale lower-resolution images to higher resolutions, boosting performance without a substantial loss in visual quality. This feature helps maintain high frame rates even in demanding games.
- Driver and Software Support: NVIDIA is renowned for its robust driver support and software features. Their drivers are frequently updated to optimize performance and fix bugs, ensuring compatibility with the latest games.
- Market Leadership: NVIDIA’s dominance in the GPU market often leads to better optimization and support from game developers, ensuring that games are tailored to leverage NVIDIA’s hardware capabilities.
Also Read: https://www.techygpu.com/2024/11/18/gpu-randomly-spikes-to-100-when-idle-2080-ti/
Is AMD a good choice for professional applications?

Yes, AMD is a strong choice for professional applications, particularly with its latest Radeon Pro and AMD Ryzen Threadripper series. AMD GPUs are known for their excellent performance in tasks such as 3D rendering, video editing, and other compute-intensive applications. They offer competitive performance and value, with features like high core counts and advanced multi-threading capabilities.
Who is the largest manufacturer of GPU?
The largest manufacturer of GPUs is NVIDIA. Founded in 1993, NVIDIA has established itself as a dominant player in the GPU market, particularly with its GeForce, Quadro, and Tesla series. NVIDIA’s GPUs are widely used in gaming, professional graphics, and data center applications.
NVIDIA’s dominance is attributed to its consistent innovation, including advancements in GPU architecture, real-time ray tracing, and AI-enhanced technologies. Their flagship products, such as the RTX 30 and RTX 40 series, are renowned for high performance and cutting-edge features, solidifying NVIDIA’s position as a leader in the GPU industry.
FAQ’s:
1. What factors should I consider when choosing a GPU manufacturer?
Consider performance, price, innovation, software support, and availability when choosing a GPU manufacturer.
2. How does Intel’s GPU performance compare to NVIDIA and AMD?
Intel’s GPUs are relatively new, with promising features but still catching up in high-end performance compared to NVIDIA and AMD.
3. What are the advantages of NVIDIA’s DLSS technology?
NVIDIA’s DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) technology enhances gaming performance by using AI to upscale lower-resolution images, improving frame rates and image quality.
4. How important are drivers and software support for GPUs?
Drivers and software support are crucial for optimal performance, compatibility, and stability of your GPU.
5. Can I use a GPU from one manufacturer with a CPU from another?
Yes, GPUs and CPUs from different manufacturers can work together, though some combinations might offer better compatibility and performance.
6. What is the impact of GPU availability on pricing?
Limited availability can drive up prices due to high demand and low supply. It’s important to monitor market conditions when purchasing a GPU.
7. How often should I upgrade my GPU?
Upgrading your GPU depends on your performance needs and the advancements in technology. Generally, upgrading every 2-4 years ensures you stay current with new features and performance improvements.
8. Are there budget-friendly GPU options from major manufacturers?
Yes, all major manufacturers offer budget-friendly options. AMD and NVIDIA provide entry-level models that balance performance and cost.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right GPU manufacturer depends on individual needs and preferences. Gamers seeking the highest performance might lean towards NVIDIA, while those looking for value for money might consider AMD. Intel’s entry into the market offers exciting possibilities for the future. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each manufacturer, you can make an informed decision that best fits your requirements.
Read More:










Post Comment